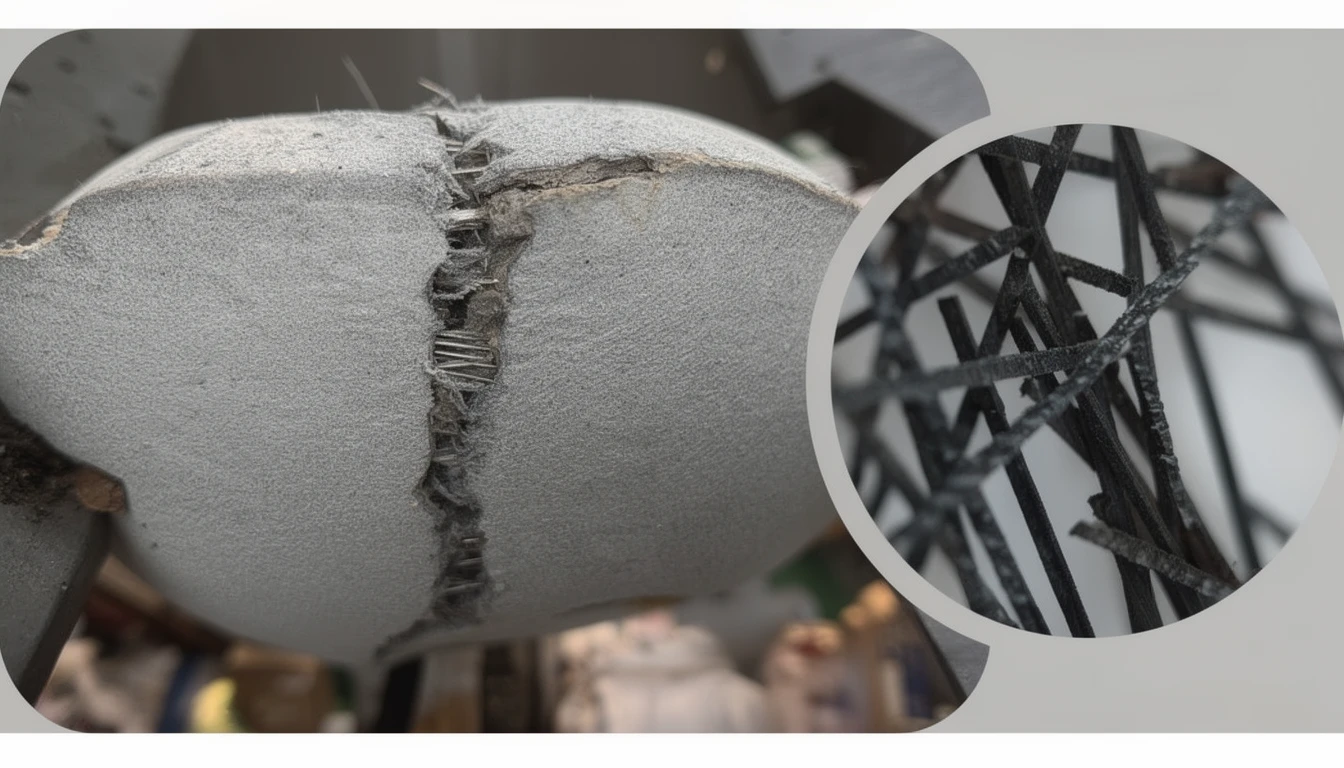
Macro-synthetic fiber is a synthetic macro fiber engineered for concrete reinforcement. It is mixed into fresh concrete. It spreads through the full volume. It helps control cracking. It also improves post-crack performance such as toughness and residual flexural strength.
Many contractors use macro-synthetic fiber to replace welded wire mesh in slabs-on-ground, or to reduce crack-related repairs in floors, pavements, shotcrete, plus some precast products.
What is macro-synthetic fiber?
Macro-synthetic fiber is a larger synthetic fiber used for concrete reinforcement. It is different from micro synthetic fiber. The main difference is size and job function. ACI guidance describes macro synthetic fibers as having a diameter (or equivalent diameter) greater than 0.3 mm.
Macro-synthetic fibers are usually made from engineered polymers such as polypropylene, polyethylene, or blends. They are produced in controlled shapes to improve anchoring in the cement matrix.
The main purpose is not only early-age crack control. The main purpose is post-crack control. The fiber helps the concrete carry load after it cracks.
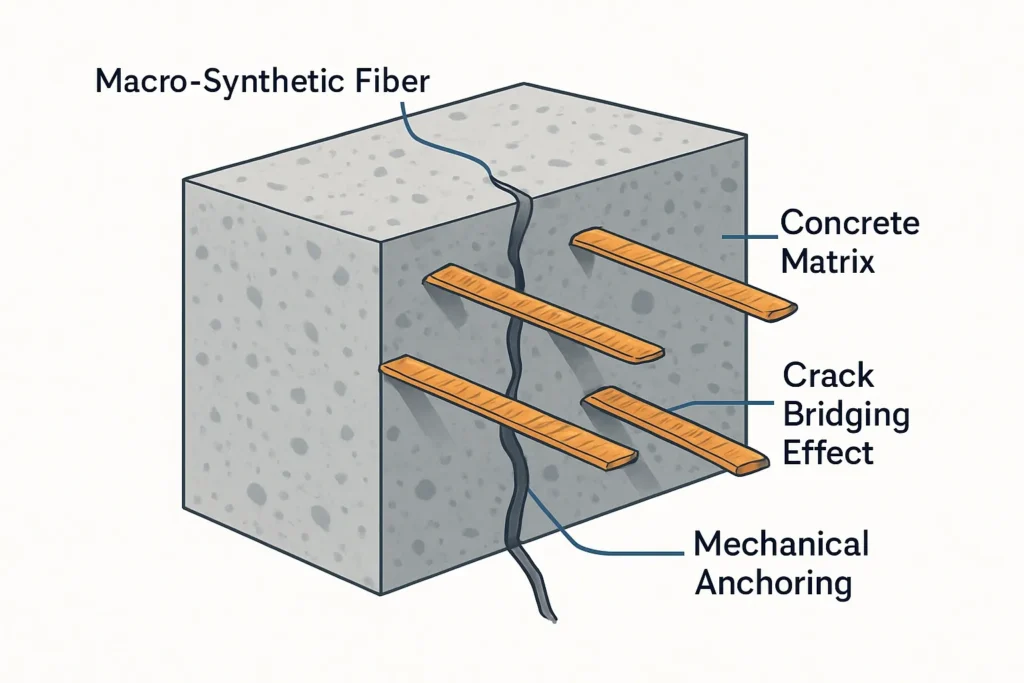
How does macro-synthetic fiber work in concrete?
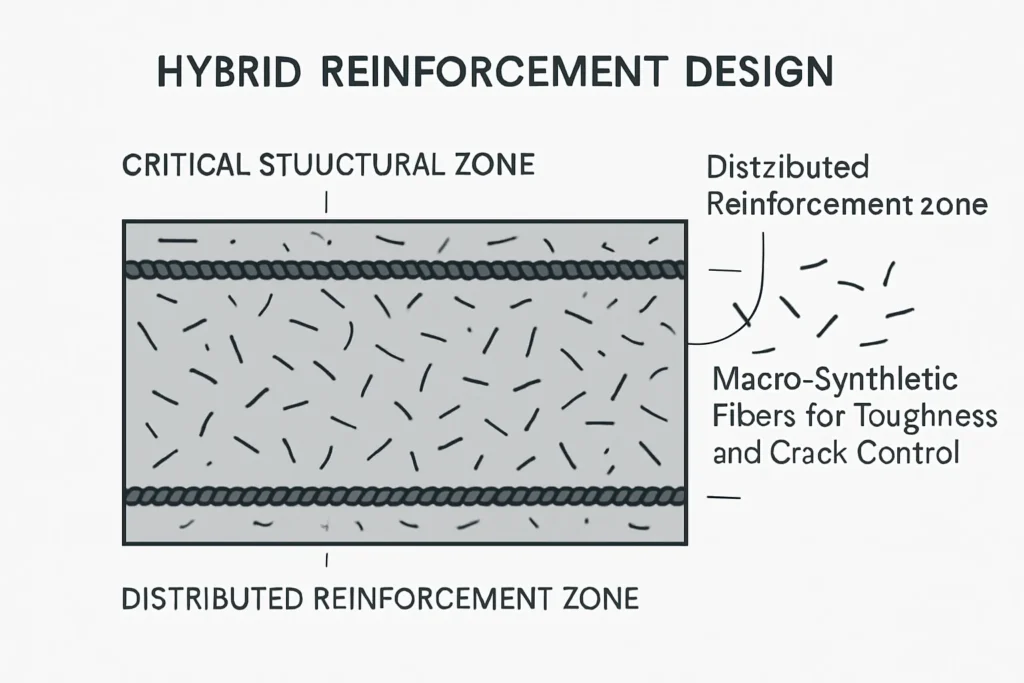
Macro-synthetic fibers work as three-dimensional reinforcement. Rebar is placed in specific zones. Fibers are mixed into the batch. That means fibers reinforce the concrete everywhere, in many directions.
When a crack forms, fibers that cross the crack help hold the crack faces together. This limits crack opening. It also improves the concrete’s ability to carry load after the first crack. Sika describes macro fibers as a tool to resist tensile stresses, control crack growth, plus increase residual flexural strength (post-cracking).
This “distributed” reinforcement changes jobsite outcomes. You often see tighter crack patterns. You also see less sudden break behavior in slabs under impact or wheel loads. The result is usually fewer surface failures at joints, edges, plus corners when the slab is designed correctly.
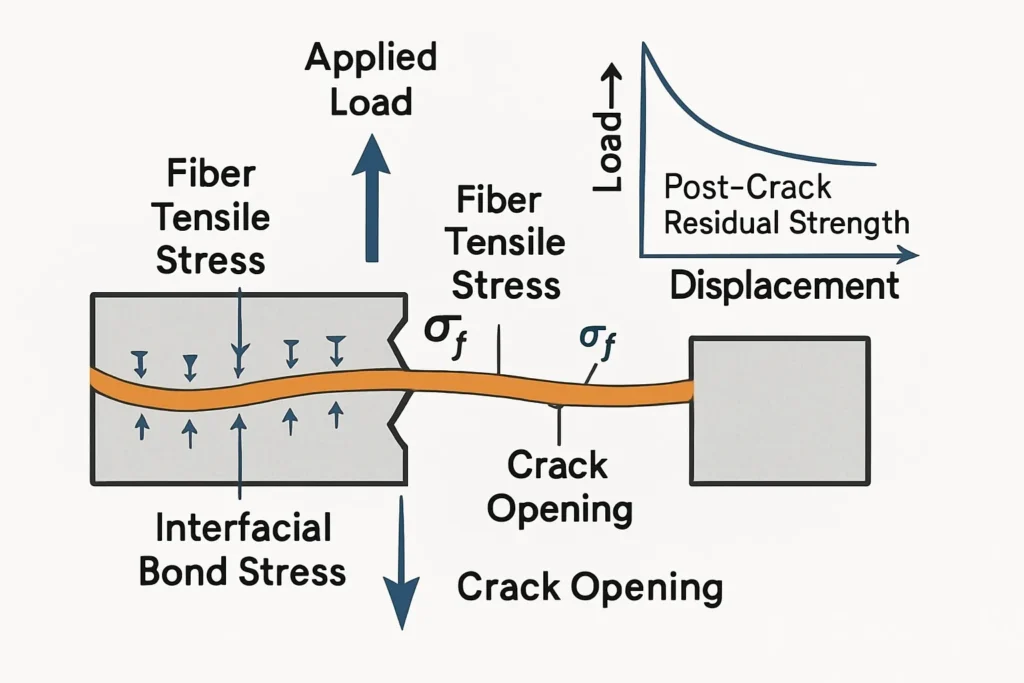
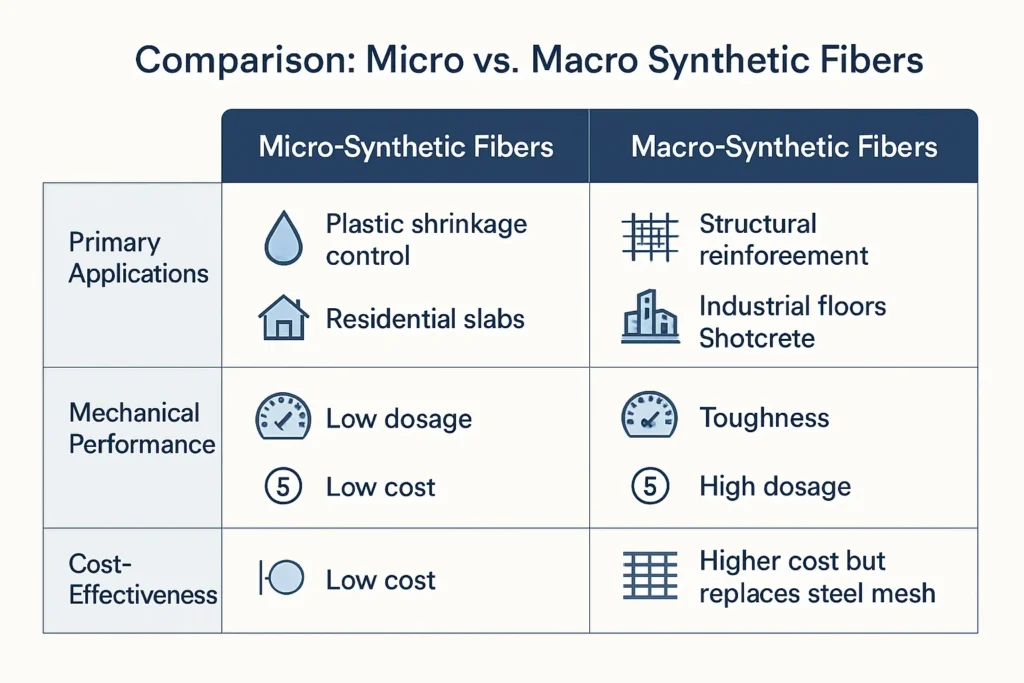
Macro vs micro synthetic fiber: what is the difference?
Micro fibers focus on fresh concrete crack control. Macro fibers focus on hardened concrete performance.
ACI guidance uses a size threshold. Micro synthetic fibers are below 0.3 mm in diameter (or equivalent). Macro synthetic fibers are 0.3 mm or greater.
Sika uses the same practical idea. It describes structural macro fibers as having diameter at or above 0.3 mm.
Typical differences you will notice:
- Micro synthetic fiber: short, fine, hair-like. Best for plastic shrinkage cracking.
- Macro-synthetic fiber: longer, thicker, higher stiffness. Best for post-crack control and toughness.
A good buying rule is simple. If your goal is fewer early hairline cracks, start with micro fiber. If your goal is post-crack load carrying and slab toughness, start with macro-synthetic fiber.
What are the main benefits of macro-synthetic fiber?
Macro-synthetic fiber is popular because it delivers practical value on real pours.
1) Better post-crack performance
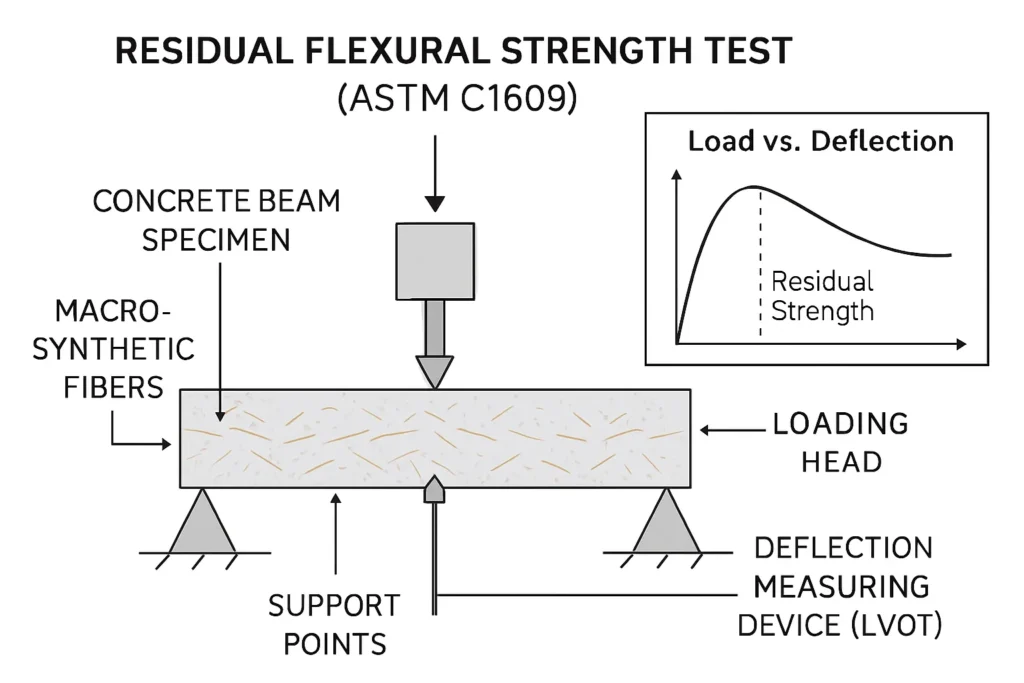
Macro fibers are used when residual flexural strength after cracking is required. ASTM C1609 is a common test reference for this type of performance.
2) Crack control that supports durability
Crack width matters. Smaller cracks reduce water entry. That supports durability, especially when steel corrosion risk is a concern.
3) Less steel handling for some slabs
Some macro fiber systems are designed to replace welded wire fabric in slabs-on-ground.
This can reduce site labor, plus improve schedule reliability.
4) Toughness under impact and repeated loads
Manufacturers position macro fibers for toughness, impact resistance, plus fatigue resistance in floors and slabs.

Where is macro-synthetic fiber used?
Macro-synthetic fibers are used when you need toughness, crack control, plus faster reinforcement workflows.
Common applications include:
- Slabs-on-ground: warehouses, logistics floors, workshops, yards
- Composite metal deck toppings: replacing wire mesh for temperature and shrinkage control in some designs
- Shotcrete: tunnels, slopes, repairs, mining support (project dependent)
- Precast concrete: thin-walled units, tanks, utility products (design dependent)
- Pavements and hardstands: where joint performance and impact resistance matter
If your project is mostly about shrinkage crack control, micro fiber may be enough. If your project needs post-crack performance, macro-synthetic fiber is often the right category to review first.

What is a typical dosage for macro-synthetic fiber?
Dosage depends on the fiber product, slab design, plus the performance target.
A common dosage band reported in technical literature is about 1.8–9.0 kg/m³ (3.0–15 lbs/yd³) for macro fibers, depending on product and application.
For composite metal decks, industry guidance cited by the Fiber Reinforced Concrete Association points to a minimum dosage of 4.0 lb/yd³ (2.4 kg/m³) for synthetic macrofibers when used for temperature and shrinkage control, under SDI ANSI guidance.
If you use low-dose synthetic fibers, NRMCA notes typical addition rates of 1–2 lb/yd³ for synthetic fibers may not require mix changes. Higher dosages can require mix adjustments.
Practical advice: do not choose dosage by habit. Use a target. Use test data when the fiber is intended to replace mesh or provide structural contribution.

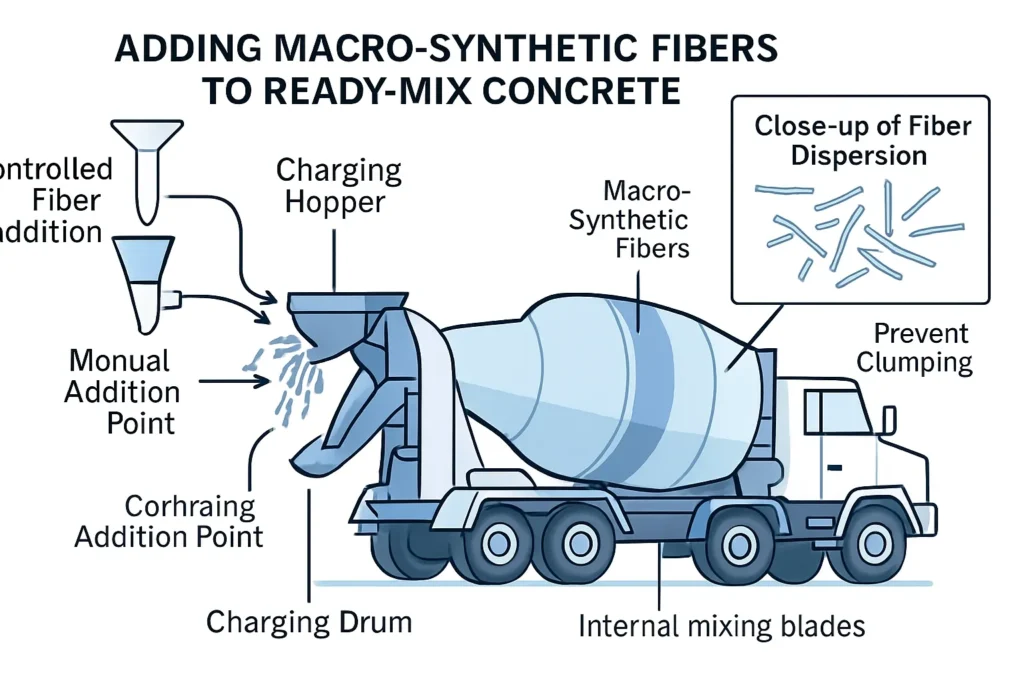
Mixing and finishing tips for macro-synthetic fiber
Macro-synthetic fiber is easy to use when the crew follows a few rules.
- Add fiber in a controlled way Do not dump all packs at once. Add gradually. This supports dispersion.
- Mix long enough for full dispersion A short mix time increases clump risk. Clumps reduce performance.
- Use admixtures to protect workability If slump drops, use a water reducer. Do not add water without control. NRMCA notes low typical synthetic fiber dosages often need no mix change. Higher dosages can change workability.
- Finish based on set, not on schedule Macro fibers can change surface feel during troweling. Good timing solves most issues.
If the project has strict visual requirements, plan a trial pour. Confirm finish quality before full production.
What are the limitations of macro-synthetic fiber?
Macro-synthetic fiber is not a universal replacement for rebar.
Key limitations to state clearly:
- Structural rebar is still required in many members such as beams, columns, suspended slabs. Codes plus engineers control this decision.
- Performance depends on dosage and design method. Replacing mesh requires equivalency checks.
- Dispersion quality matters. Poor mixing can create weak zones.
- You need the right tests for performance claims. Post-crack claims are often supported with residual strength testing.
The safe approach is simple. Use macro fibers to improve toughness and crack control. Use rebar where the design needs defined tensile capacity.
What standards apply to macro-synthetic fiber?
If you are writing specs, standards matter.
Helpful references include:
- ASTM C1116: defines fiber-reinforced concrete categories. Type III covers synthetic fiber-reinforced concrete, with required durability evidence in cement alkalinity.
- ACI 544.3R: provides guidance and definitions for synthetic fibers, including the micro vs macro diameter threshold.
- ASTM C1609: commonly used to evaluate residual flexural performance for fiber reinforced concrete. Sika points to this when discussing macro fiber use for post-crack strength.
A practical spec checklist:
- Define the application (slab, deck, shotcrete, precast).
- Define the goal (shrinkage crack control, residual strength, toughness).
- Reference the standard (ASTM C1116 Type III, plus relevant performance tests).
- Require product data plus test reports for the stated goal.
- Require mixing instructions plus QC plan.
Expert guidance from Ecocretefiber™
Macro-synthetic fiber selection is simple when the goal is clear. The details still matter. Fiber shape matters. Dosage matters. Mixing energy matters. Testing method matters.
Ecocretefiber™ provides general support first. We help you match the fiber to your real problem. Then we move to product selection.
What support usually looks like:
- Fiber selection: micro vs macro, plus product form options
- Dosage suggestion based on slab type, service loads, plus target function
- Mixing and finishing tips to improve dispersion and surface quality
- Documentation support for bids and distributor catalogs
- Project matching, plus basic compliance references (ASTM C1116 Type III when relevant)
Brand and company: Ecocretefiber™ | Shandong Jianbang Chemical Fiber Co., Ltd.
If you want to develop a stable fiber line, we also support distributor cooperation. If you want a project quote, we can support trial planning, plus repeat supply.
Conclusion
Macro-synthetic fiber is a structural synthetic fiber mixed into concrete to improve crack control, toughness, plus post-crack performance. It is larger than micro fiber. ACI guidance uses 0.3 mm as a practical size break between micro and macro synthetic fibers.
Macro-synthetic fiber is often used in slabs-on-ground, decks, shotcrete, plus precast, especially when the goal is better residual performance or when reducing mesh labor is valuable. Dosage should follow your application and design method, with common dosage ranges varying widely by product and use case.
If you want fewer crack issues, better slab toughness, plus a cleaner reinforcement workflow, macro-synthetic fiber is a strong option to evaluate.


